How sugar cane products Have Become Essential in the Food and Beverage Sector
Discover Everything About Sugar Cane: From Production Strategies to Product Innovations
Sugar cane is a crop with both historic relevance and modern importance. Its farming has evolved from traditional methods to modern techniques that satisfy today's farming demands. This advancement consists of cutting-edge processing techniques that change the cane into a selection of products. As the sector faces ecological challenges, brand-new sustainable techniques are emerging. The complexities of sugar cane production and its future in worldwide markets present intriguing concerns worth discovering even more.
The History of Sugar Cane Cultivation
Sugar cane is commonly linked with exotic climates, its growing has an abundant history that dates back thousands of years. Coming From in Southeast Asia, the earliest documents of sugar cane's usage date back to around 8000 BCE, where it was eaten for its sweet taste. By the very first millennium, it infected India, where it became essential to neighborhood societies. The modern technology to take shape sugar arised in India by the fifth century CE, noting a considerable turning point in sugar production.With the expansion of profession routes, sugar cane located its way to the Middle East and, at some point, Europe. The establishment of haciendas in the Caribbean during the 16th century changed the worldwide sugar market, driven greatly by colonial growth. As sugar became an in-demand product, its cultivation shaped economic situations and cultures, preparing for modern manufacturing strategies that progressed with the advancement of farming and modern technology.
Conventional Farming Strategies
As sugar cane cultivation developed with background, conventional farming strategies arised as fundamental techniques that formed its manufacturing. These techniques, typically given through generations, consisted of making use of handbook tools such as hoes and machetes for planting and harvesting. Farmers typically prepared the soil by hand, making use of plant rotation and intercropping to keep dirt fertility and control parasites. Water monitoring was vital, with numerous typical cultivators counting on all-natural watering systems and rain harvesting.Planting was most of the time to correspond with seasonal rainfalls, guaranteeing ideal development problems. Generally, sugar cane was planted in rows, permitting for easier maintenance and harvesting. Harvesting was done manually, calling for knowledgeable labor to lessen damages to the stalks. In general, typical farming methods highlighted sustainability and a deep understanding of the local setting, forming an essential component of the cultural heritage surrounding sugar cane agriculture. These practices prepared for future innovations in sugar manufacturing.
Modern Agricultural Practices
Modern farming techniques have significantly bundled accuracy farming methods to improve sugar cane production. sugar cane products. These methods make use of data-driven techniques to optimize inputs and improve yields while minimizing environmental effect. Additionally, lasting insect monitoring approaches are being embraced to safeguard plants without compromising eco-friendly balance
Accuracy Farming Techniques
Precision farming strategies stand for a transformative approach to farming, leveraging technology to enhance performance and sustainability in sugar cane manufacturing. By using tools such as GPS, remote sensing, and information analytics, farmers can monitor crop health, soil problems, and water use with unmatched accuracy. This data-driven approach permits targeted interventions, decreasing waste and maximizing source appropriation. Drones and satellite images promote real-time assessments, allowing cultivators to react promptly to arising issues or changes in ecological problems. Additionally, precision farming enhances return projecting and boosts decision-making procedures, eventually bring about better crop monitoring. Consequently, sugar cane manufacturers can achieve higher effectiveness and profitability while lessening their ecological footprint, adding to the total advancement of modern farming methods.
Sustainable Bug Management
Effective monitoring of parasites is vital for maintaining the wellness and productivity of sugar cane plants. Sustainable parasite administration practices concentrate on decreasing chemical inputs while making best use of environmental equilibrium. sugar cane products. Integrated Parasite Monitoring (IPM) is a preferred strategy, combining biological control, habitat manipulation, and using resistant sugar cane ranges. Farmers are progressively using advantageous pests and all-natural predators to suppress pest populaces, minimizing dependence on synthetic pesticides. Surveillance parasite levels via traps and hunting enables prompt treatments, ensuring that control actions are used just when necessary. In addition, crop rotation and intercropping improve biodiversity, additional diminishing bug break outs. By taking on these lasting practices, sugar cane producers can maintain crop yield while advertising environmental stewardship and lowering the negative effects related to Visit This Link traditional insect control approaches
Handling Sugar Cane: From Field to Factory
The detailed trip of sugar cane from field to factory involves numerous essential steps that change this lively crop into a resources for sugar production. After harvesting, sugar cane is promptly transferred to the handling facility to minimize sucrose loss. The first step at the factory is cleaning the cane to eliminate contaminations, complied with by crushing to extract the juice. This juice undergoes explanation, where it is heated and treated with lime to eliminate solid particles and impurities.Once clarified, the juice is concentrated via evaporation, resulting in syrup. The syrup is after that crystallized by cooling and including seed crystals, leading to the development of sugar crystals. Complying with condensation, the sugar goes through centrifugation to separate it from molasses. Eventually, the sugar is dried, packaged, and prepared for circulation. Each action in this procedure is vital for making certain the quality and performance of sugar production.
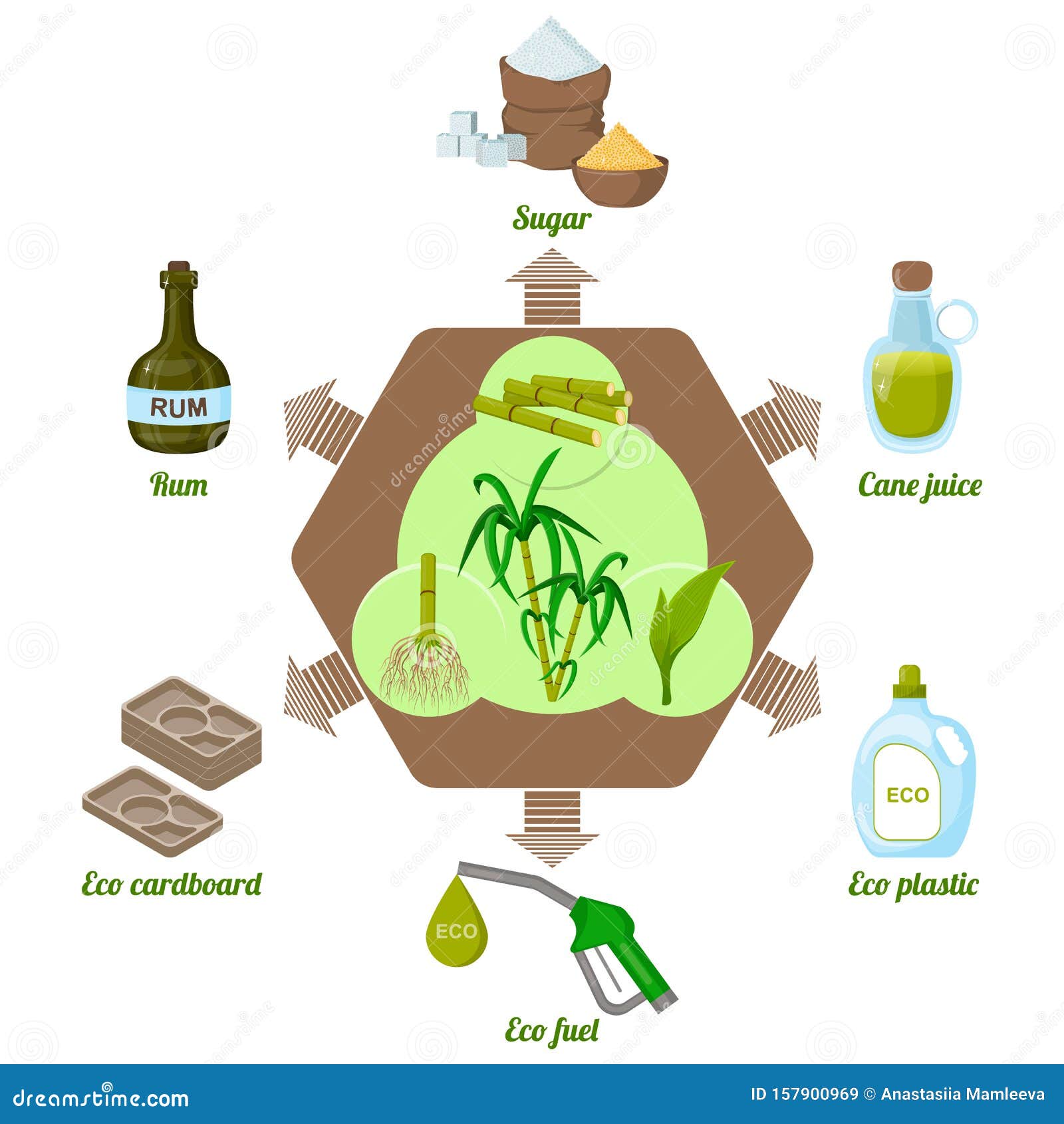
Sugar Cane Products and Their Applications
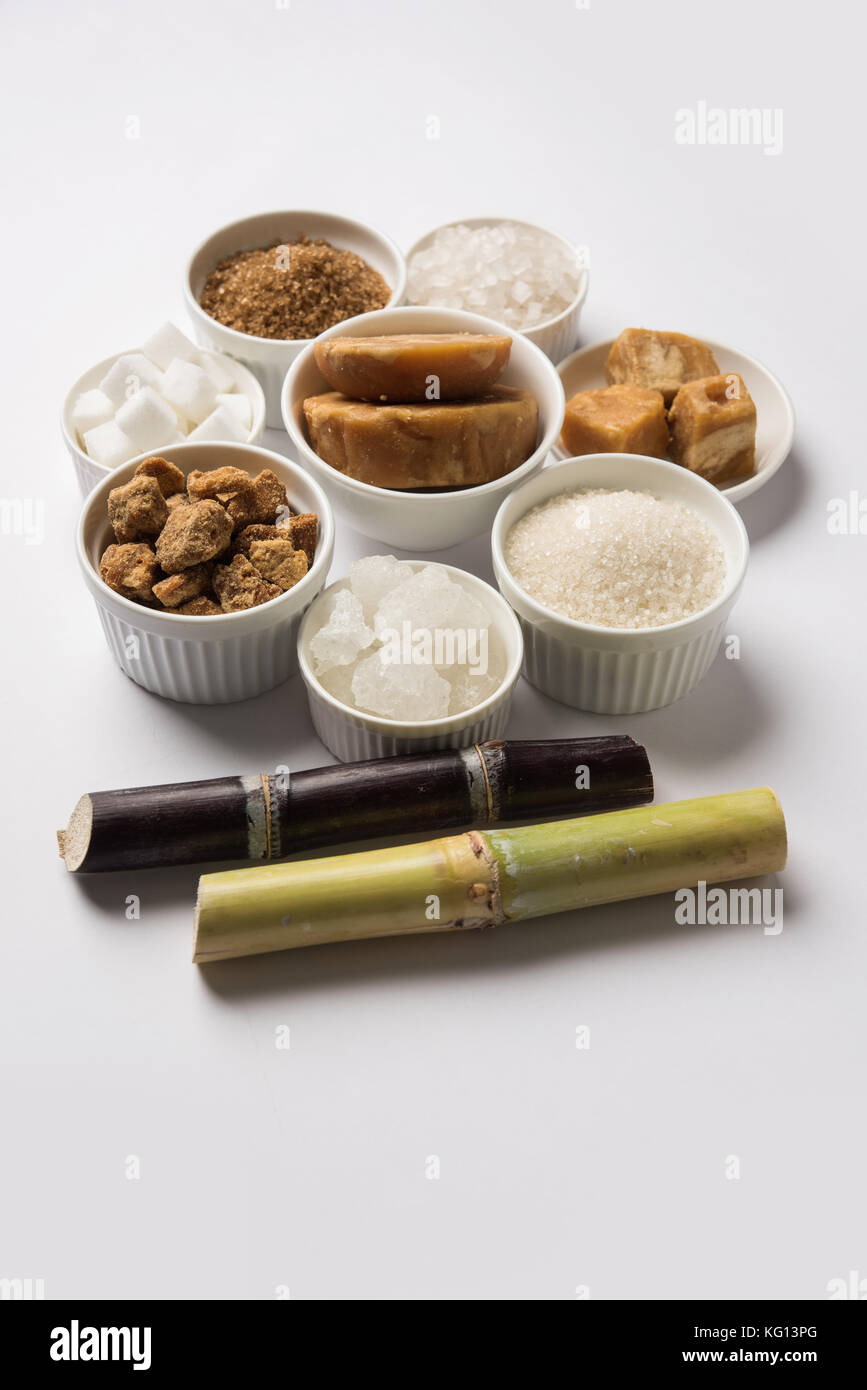

Sweeteners and All-natural Sugars
Typically neglected, sweeteners and all-natural sugars derived from sugar cane play a crucial function in the food and beverage sector. These products, including sucrose, molasses, and raw sugar, supply a variety of tastes and functionalities that enhance numerous food products. Sucrose, one of the most common sugar, is widely used for its sweetening residential properties, while molasses contributes depth and complexity to baked products and sauces. Natural sugars from sugar cane are favored for their marginal processing and viewed wellness advantages compared to synthetic sweeteners. Additionally, innovations in sugar cane handling have actually led to options like liquid sugar and focused cane juice, satisfying diverse customer preferences. Overall, sugar cane-derived sugar are indispensable to flavoring, maintaining, and enhancing food experiences.
Biofuels and Renewable Resource

Sustainability in power manufacturing has progressively transformed attention to sugar cane as a practical resource for biofuels. This tropical crop, abundant in sucrose, can be transformed right into ethanol, a sustainable fuel that lowers greenhouse gas exhausts compared to nonrenewable fuel sources. The fermentation procedure utilizes molasses, a byproduct of sugar manufacturing, making the most of resource effectiveness. Sugar cane's biomass, consisting of bagasse and leaves, can be transformed right into bioenergy, adding to a circular economic climate. Different innovations in handling strategies enhance the return of biofuels, making sugar cane an appealing choice for energy diversification. Furthermore, the growing demand for lasting energy resources drives research into improving cultivation techniques and minimizing the carbon footprint of biofuel manufacturing, placing sugar cane as a article principal in the renewable resource landscape.
Developments in Sugar Cane Sustainability
As the international need for sugar rises, technologies in sugar cane sustainability have actually become important to fulfill both ecological and financial difficulties. Modern agricultural techniques are being applied to minimize water usage, improve soil wellness, and minimize chemical inputs. Strategies such as precision farming make use of information analytics and innovation to optimize source use and increase plant returns sustainably.Additionally, the development of genetically modified sugar cane ranges aims to boost resistance to parasites and ecological stressors, resulting in higher efficiency with less inputs. Waste monitoring techniques are additionally progressing; by-products from sugar cane handling are being transformed right into bioenergy, decreasing reliance on fossil fuels.Furthermore, collaborations between agricultural stakeholders and ecological companies are fostering methods that advertise biodiversity and ecological community wellness. These developments not only help reduce the ecological effect of sugar cane manufacturing however additionally develop a more resilient and lasting industry for the future.
The Future of Sugar Cane in Global Markets
While worldwide sugar consumption proceeds to increase, the future of sugar cane in global markets encounters both opportunities and challenges. The enhancing demand for biofuels and lasting items provides a substantial chance for sugar cane producers, as the crop can be made use of for ethanol production and other environment-friendly alternatives. Furthermore, innovations in processing strategies might improve performance and reduce expenses, making sugar cane a lot more competitive versus other sweeteners.However, obstacles such as environment modification, rising and fall market prices, and changing consumer choices towards much healthier options complicate the landscape. Moreover, trade policies and tolls can influence the international market dynamics, affecting farmers' productivity. As stakeholders browse these intricacies, collaboration among manufacturers, governments, and researchers will be important in adapting to the developing market. The future of sugar cane depends upon stabilizing these chances and obstacles to protect its place in a rapidly transforming international economy.
Often Asked Concerns
How Does Sugar Cane Impact Resident Ecosystems and Biodiversity?
The growing of sugar cane considerably influences regional environments and biodiversity. Monoculture techniques can cause habitat destruction, while chemical use might damage non-target varieties, ultimately interrupting environmental equilibrium and minimizing species richness in influenced areas.
What Are the Health And Wellness Effects of Consuming Sugar Cane Products?
The health effects of consuming sugar cane items consist of possible benefits like energy boosts and antioxidants, yet too much consumption may cause weight gain, oral concerns, and boosted threat of diabetes, prompting moderation in consumption.
Exist Any Type Of Alternatives to Sugar Cane for Sugar Manufacturing?
Alternatives to sugar cane for sugar manufacturing consist of sugar beet, maple sap, and coconut palm sap. These resources give similar sweetness and can be cultivated in various environments, using varied options for sugar manufacturing worldwide.
Exactly How Is Sugar Cane Affected by Environment Change?
Climate change considerably influences sugar cane, causing click here now altered rains patterns, boosted temperature levels, and heightened bug stress. These elements can reduce returns and impact general high quality, triggering the requirement for flexible agricultural methods to guarantee sustainability.
What Are the Labor Conditions for Sugar Cane Workers Internationally?
Labor problems for sugar cane employees globally differ significantly, usually identified by low earnings, long hours, and insufficient safety and security procedures. Lots of face exploitation and rough functioning environments, particularly in creating countries reliant on sugar cane manufacturing.